
Background: Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis and regulates iron metabolism. In Phase 3 trials, roxadustat increased hemoglobin (Hb) levels and reduced the number of red blood cell (RBC) transfusions vs placebo in patients with anemia of non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (CKD). In anemia of dialysis-dependent CKD, roxadustat achieved greater mean Hb increase vs epoetin alfa, and reduced IV iron use and RBC transfusions (Coyne, et al. Poster SA-0228 American Society of Nephrology (ASN) 2019; Charytan, et al. Poster SA-0227 ASN 2019)
Low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (LR-MDS), characterized by symptomatic anemia, is treated with RBC transfusion, erythropoiesis-stimulation agents (ESAs), or luspatercept. Suboptimal response and response durability across MDS subpopulations demonstrates an unmet medical need in LR-MDS. We report a 52-week update of the open-label (OL) phase of a study of roxadustat in anemia in primary MDS patients that determined the starting dose of the ongoing double-blind study phase (NCT03263091).
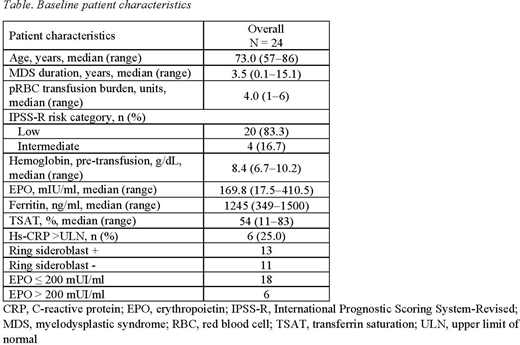
Methods: The OL phase (N=24) used 3 sequential dose cohorts (1.5, 2.0, and 2.5 mg/kg) thrice weekly (TIW). Eligible patients had very low- to intermediate-risk primary MDS patients per International Prognostic Scoring System-Revised classification, with < 5% bone marrow blasts; baseline Hb < 10.0 g/dL; had low transfusion burden, defined as receiving 1-4 RBC units within 8 weeks before randomization; endogenous EPO levels ≤ 400 mIU/mL; and no 5q(del) cytogenetic abnormality. Red blood cell transfusion was allowed per institutional criteria. Roxadustat doses were titrated every 8 weeks based on Hb response and RBC transfusions. The primary endpoint was transfusion independence (TI) for ≥ 56 consecutive days during the first 28 treatment weeks; follow-up was at 52 weeks. Secondary endpoints included TI ≥ 56 consecutive days anytime during the study, proportion of patients who achieved ≥ 50% reduction in number of RBC transfusion over any 8 weeks vs baseline (BL), cumulative number of patient-exposure-week of TI, cumulative number of pRBC packs transfused, proportion of patients who achieved TI for > 20 weeks. Safety was assessed via adverse events monitoring and patients (%) who progressed to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Patients with and without ring sideroblasts (RS+/RS-) and BL EPO ≤ 200 mIU/ml and > 200 mIU/ml were assessed for the primary endpoint.
Results: In the OL phase, 24 transfusion-dependent LR-MDS patients were enrolled in 3 starting dose cohorts (Table). Nine patients (38%) achieved TI for ≥ 56 consecutive days within the first 28 and 52 weeks, 3 in cohort 1 (1.5 mg/kg), 1 in cohort 2 (2.0 mg/kg), and 5 in cohort 3 (2.5 mg/kg). When TI was achieved, 78% were receiving 2.5 mg/kg dose, 11% were receiving 2.0 mg/kg dose (started with 1.5 mg/kg) and 11% were receiving 1.5 mg/kg. Four patients (16.7%) remained TI for > 20 weeks (1 at 1.5 mg/kg dose level and 3 at 2.5 mg/kg dose-level) at 52 weeks. The 50% reduction in number of transfusion compared with BL occurred in 13 patients (54.2%) at 28 weeks and 14 (58.3%) at 52 weeks. In patients with TI duration ≥ 56 days (n = 9), the mean (SD) TI duration was 182.9 (153.66) days. In patients with TI duration ≥ 140 days (n = 4), the mean (SD) TI duration was 324.5 (121.22) days. Subgroups met the primary endpoint at week 28 (23.1% and 54.5% MDS-RS+ and -RS-, respectively, and 38.9% and 33.3% BL EPO ≤ 200 mIU/ml and > 200 mIU/ml, respectively); all subgroups maintained TI response to week 52. The overall safety profile was consistent with this patient population. Eight patients reported 8 treatment-emergent serious AEs; none were fatal. No patient progressed to AML.
Conclusion: In this 52-week update, roxadustat 2.5 mg/kg TIW was effective in LR-MDS patients, based on observed response (TI and transfusion reduction), safety profile, and durable 52-week response. The ongoing, 156-patient, double-blind study phase uses a 2.5 mg/kg starting dose. Preliminary data in OL subgroups RS-/RS + and BL EPO ≤ 200 mIU/ml and >200 mIU/ml suggest roxadustat may be effective in these subgroups. These data await confirmation in the ongoing double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Carraway:Abbvie: Other: Independent Advisory Committe (IRC); ASTEX: Other: Independent Advisory Committe (IRC); Takeda: Other: Independent Advisory Committe (IRC); Stemline: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Other: Research support, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Bradley:FibroGen, Inc.: Current Employment. Saha:FibroGen, Inc.: Current Employment. Bartels:FibroGen, Inc.: Current Employment. Leong:FibroGen Inc.: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. Yu:FibroGen, Inc.: Current Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal